Pelvic Organ Prolapse
$ 20.99 · 4.8 (670) · In stock
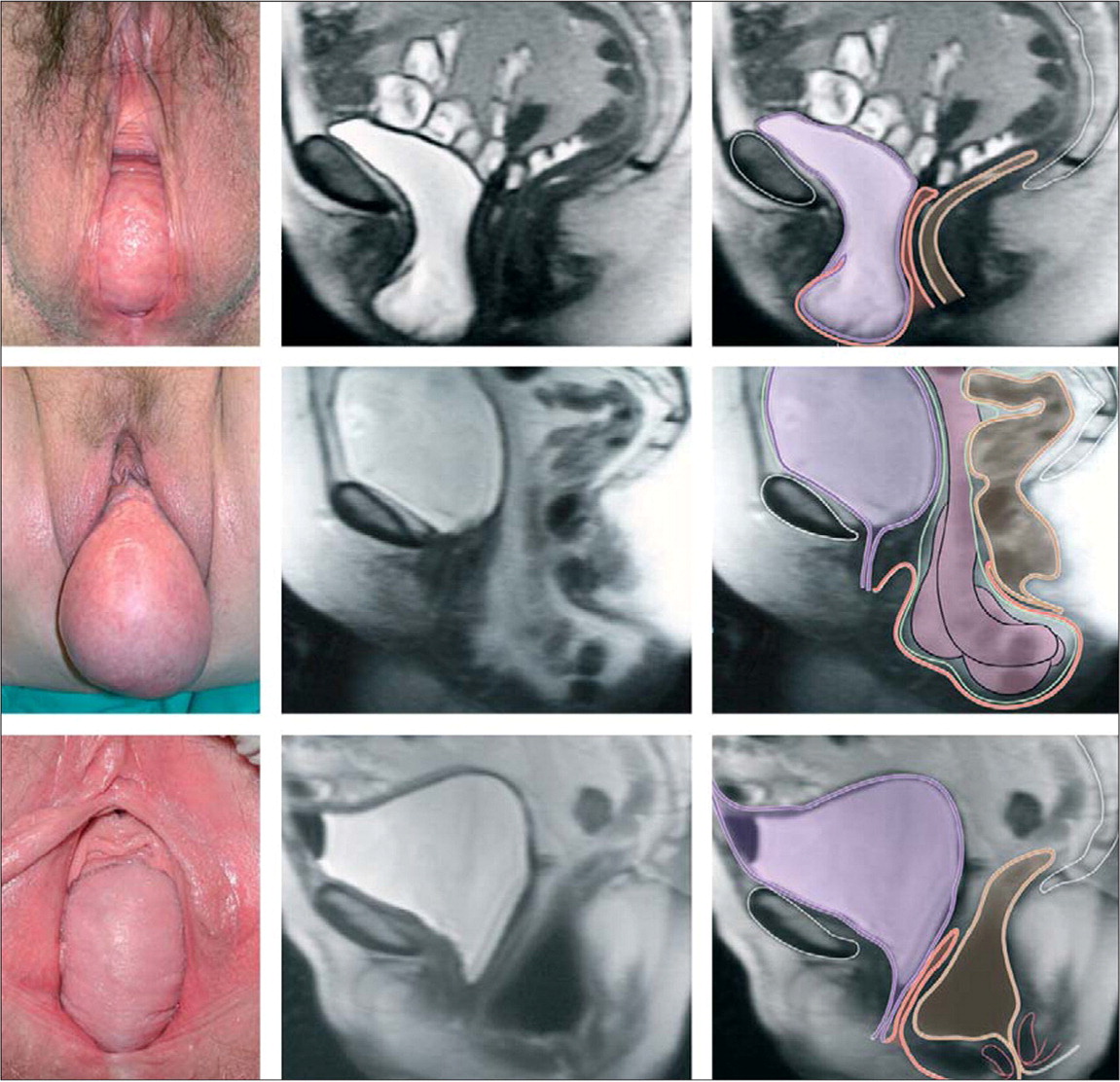
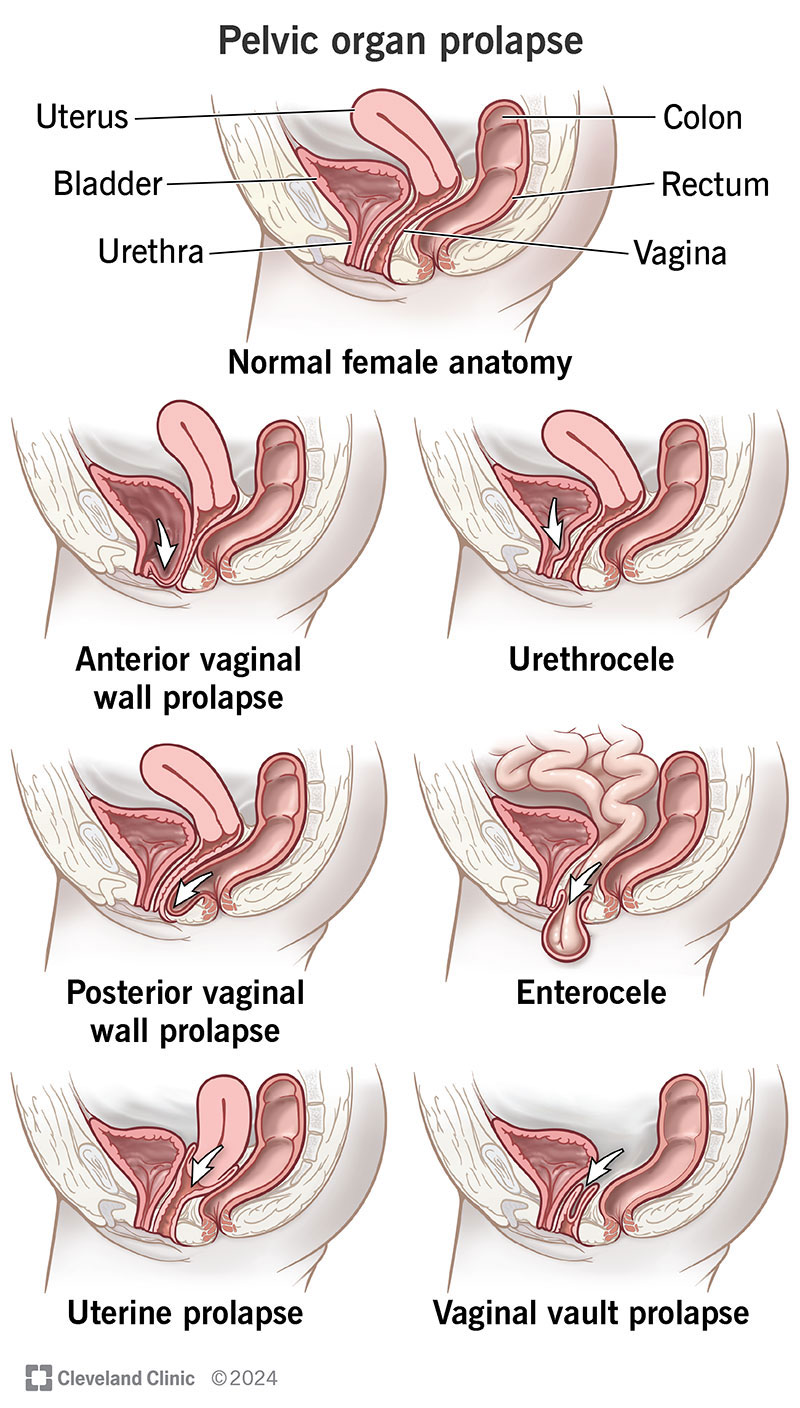
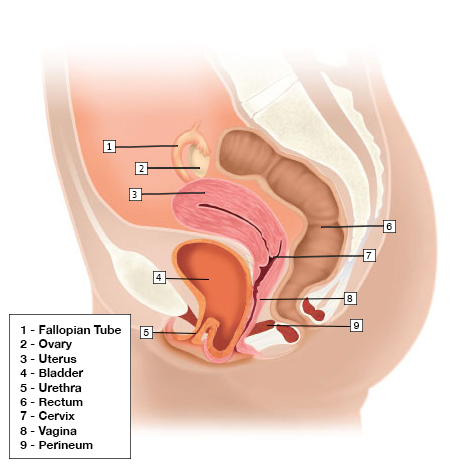
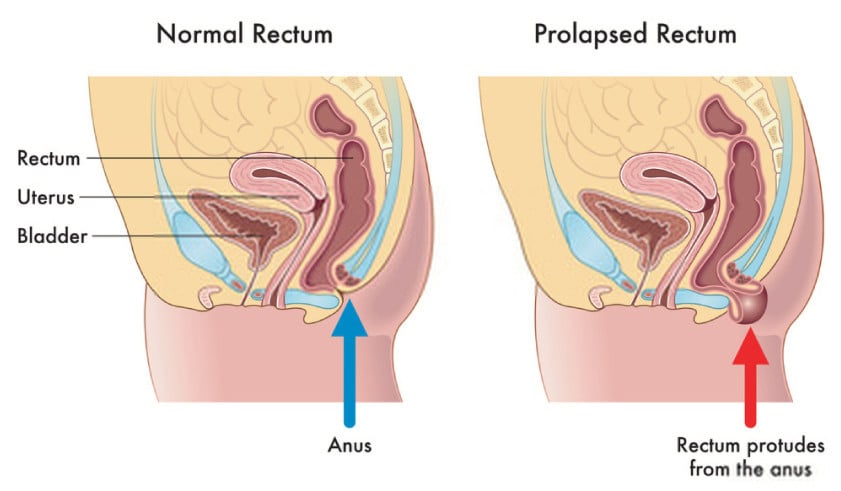
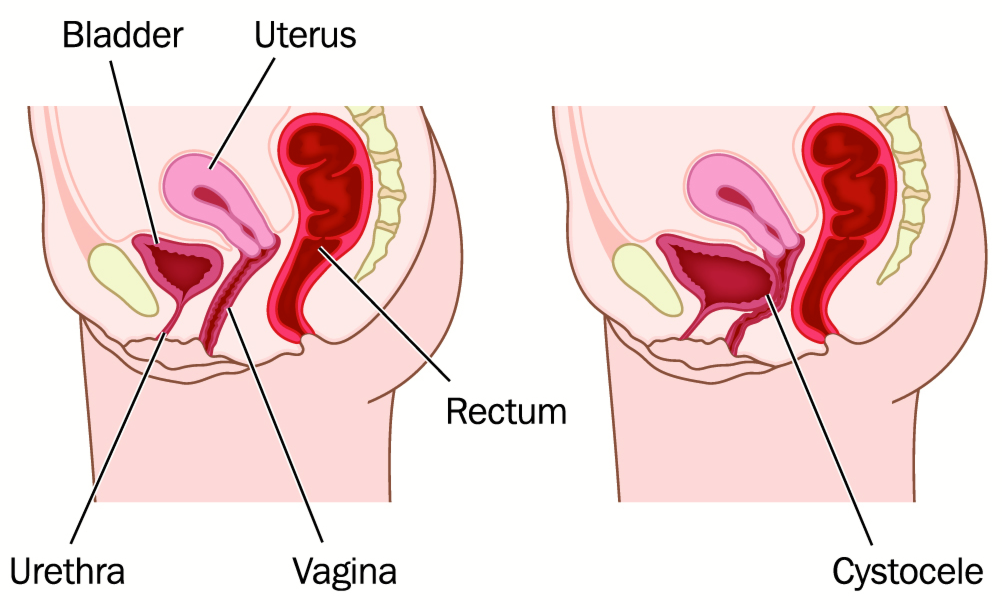
Pelvic organ prolapse is the descent of one or more of the anterior vaginal wall, posterior vaginal wall, the uterus (cervix), or the apex of the vagina (vaginal vault or cuff scar after hysterectomy). Prevalence increases with age. The cause of prolapse is multifactorial but is primarily associated with pregnancy and vaginal delivery, which lead to direct pelvic floor muscle and connective tissue injury. Hysterectomy, pelvic surgery, and conditions associated with sustained episodes of increased intra-abdominal pressure, including obesity, chronic cough, constipation, and repeated heavy lifting, also contribute to prolapse. Most patients with pelvic organ prolapse are asymptomatic. Symptoms become more bothersome as the bulge protrudes past the vaginal opening. Initial evaluation includes a history and systematic pelvic examination including assessment for urinary incontinence, bladder outlet obstruction, and fecal incontinence. Treatment options include observation, vaginal pessaries, and surgery. Most women can be successfully fit with a vaginal pessary. Available surgical options are reconstructive pelvic surgery with or without mesh augmentation and obliterative surgery.
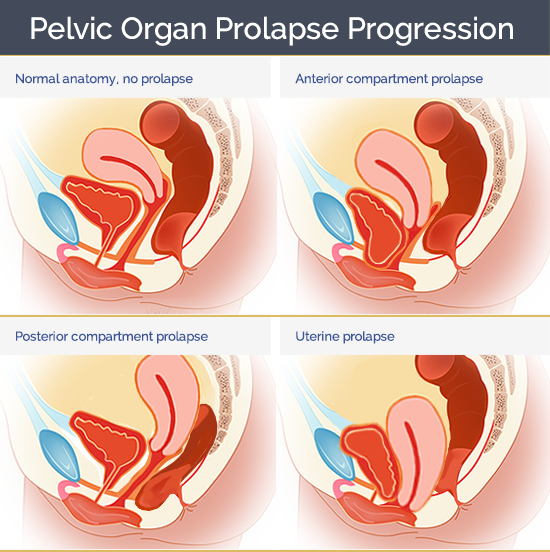
Pelvic Organ Prolapse

JPM, Free Full-Text
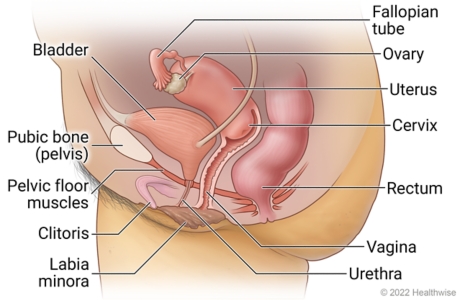
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
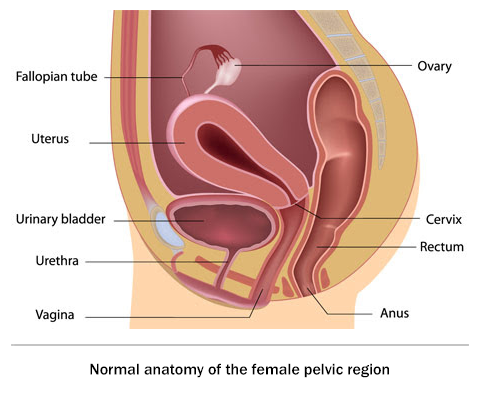
What is Pelvic Organ Prolapse? Types, causes and treatment
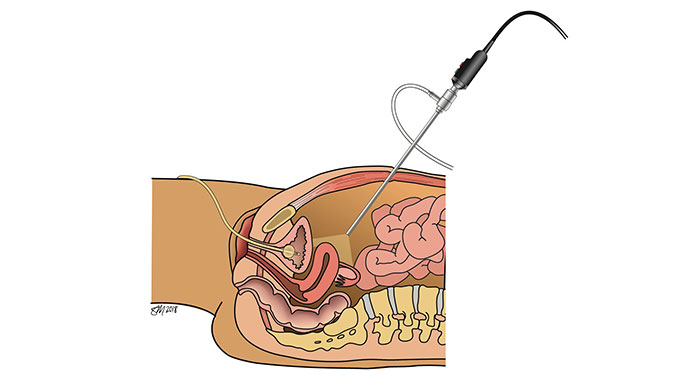
Pelvic Organ Prolapse - UChicago Medicine

Diagnosis and management of pelvic organ prolapse: The basics - Women's Healthcare

Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Diagnosis and Treatment
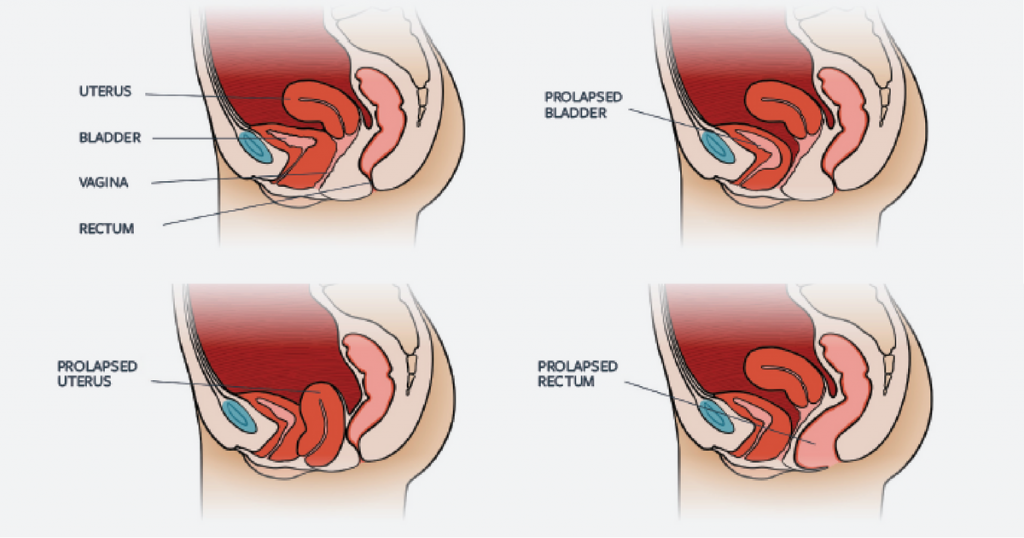
Pelvic Organ Prolapse - 5 Considerations For Training With POP

Can pelvic organ prolapse be a sign of cancer?
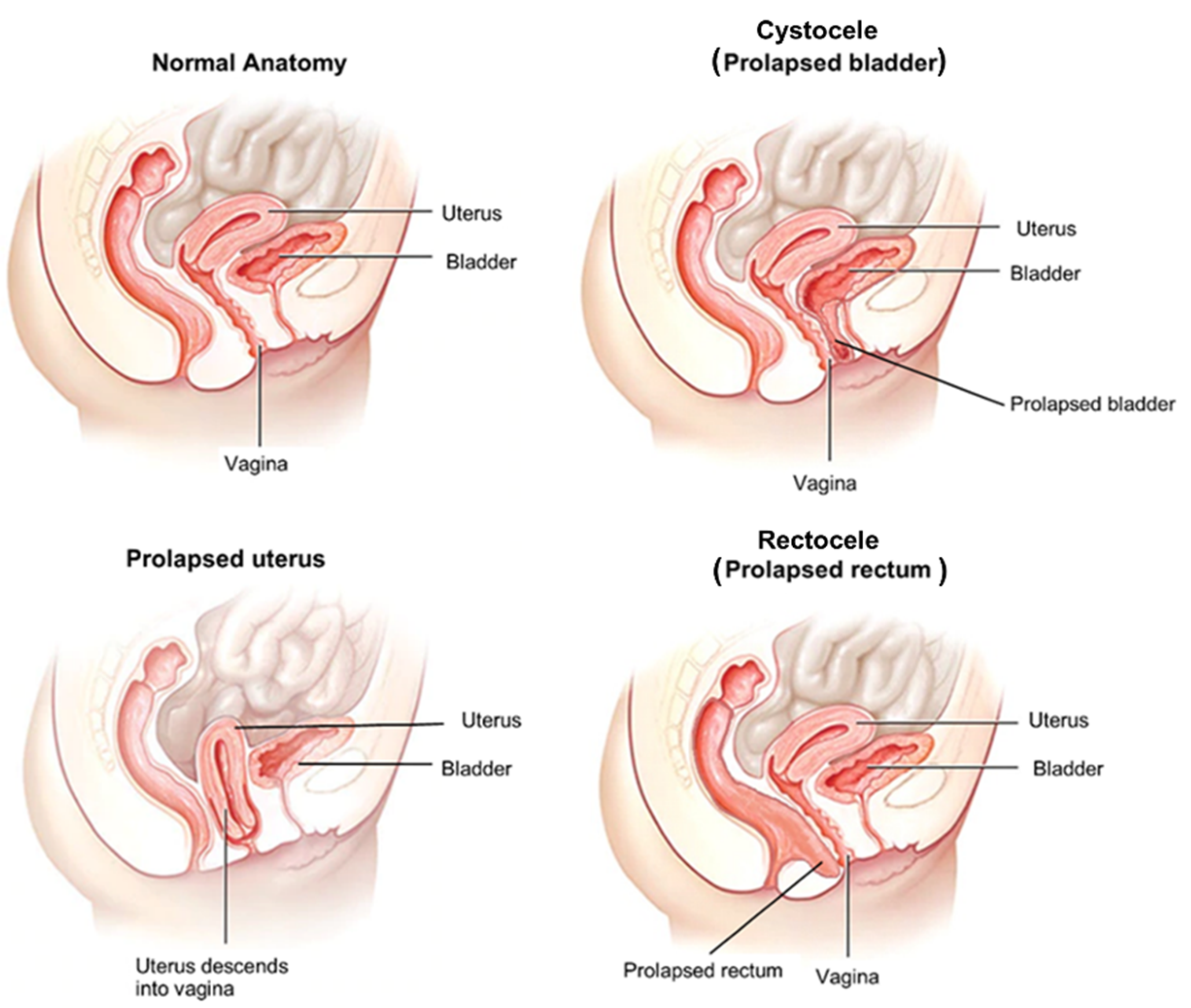
Biomolecules, Free Full-Text
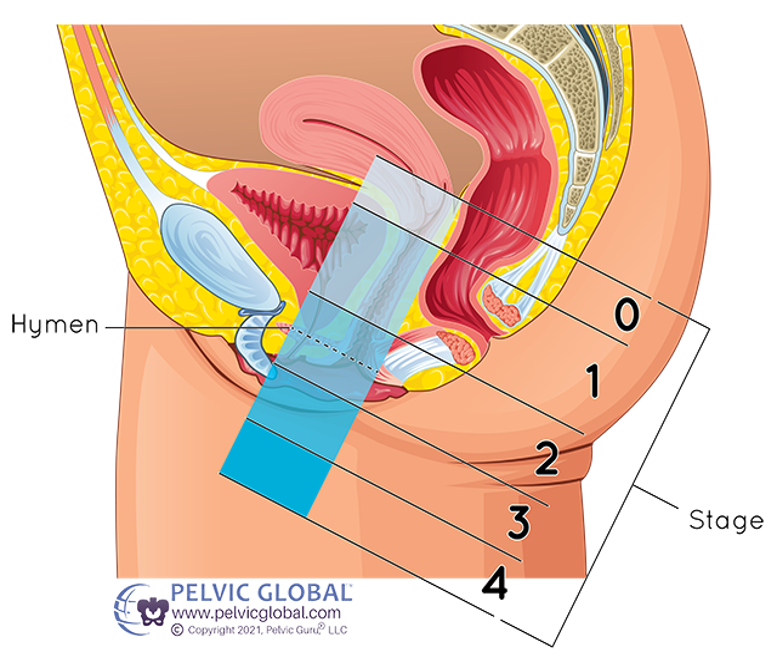
Understanding & Treating Pelvic Organ Prolapse - ProNatal Fitness
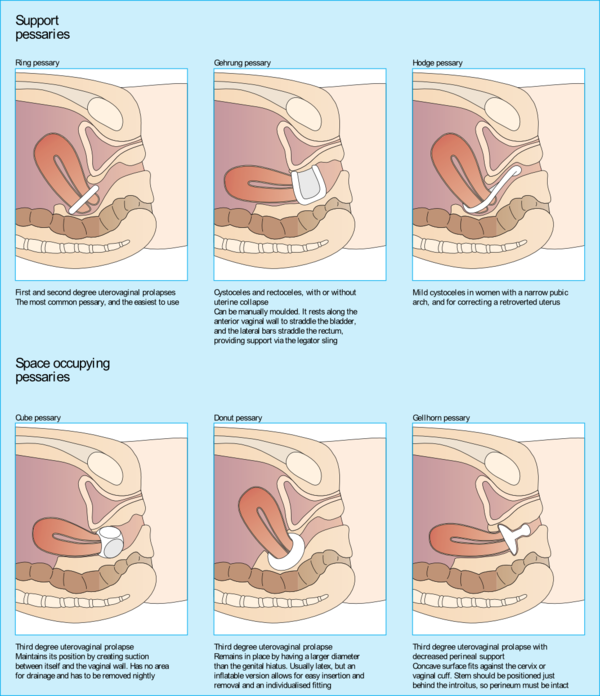
Uterine Prolapse - Physiopedia
What is Pelvic Organ Prolapse? Types of Prolapse, Diagnosis, Treatment
Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment